PeakLab v1 Documentation Contents AIST Software Home AIST Software Support
Section Data
This Section Data option is used to section data into active and inactive regions. Only active regions are are scanned for peaks, and only active points are fitted.
The Section Data button or the Section item in the main window Data menu opens the sectioning procedure.
![]() You can also use the Section icon in the main program toolbar.
You can also use the Section icon in the main program toolbar.
You can also invoke the sectioning for an individual data set by right clicking the data set of interest in the main program window and selecting Independently Section this Data Set from the popup menu.
Sectioning
A PeakLab Graph will be rendered for each of the data sets in the current file. Each graph will be scaled for only the active points, those used within peak fitting. Inactive points are shown in the current inactive point color and with a different graph background color. You may section for active or included bands, or inactive or excluded bands, numerically or by using the mouse.
All of the data sets will be present in this sectioning procedure, irrespective of whether or not the data is selected in the main window.
Data Levels and Sectioning
Each level of the data in the PeakLab file has its own specific sectioning. In general, you will use this Section Data procedure to section the uppermost (current) level of data.
Unlike the other preprocessing options, such as the Transform Data, Subtract Baseline, and IRF Deconvolution, which are only available to the topmost level of data, you can select the Section Data button from any level of data. If you alter the state of the data in a resectioning, however, you will void all fits that were assigned to that level.
A subsequent level inherits the sectioning from its precursor. Revising the sectioning in an interior data level affects only that level. The sectioning in the subsequent levels is not altered.
Sectioning and Fitting a Different Set of Peaks
If you wish to process and fit an entirely different set of peaks, you can use the Copy option in the main window to create a copy of any data level in the existing sequence. That level can then be sectioned and those specific peaks independently fitted with no additional preparation steps, assuming the transform, baseline, and deconvolution are already represented in the level copied. In most cases, you should have a few levels available for additional sectioning and fits.
If you need more than the eight levels presently stored in the PeakLab data structure, you can save the current PDF data file, select the the last level applicable to this next step, and then use the Revert option in the main window to clear all data levels above this one.
![]() If you revert to a sectioned level, you may need to use the Include Inactive Data in Scaling option
in the toolbar of the graph (or the Show Inactive checkbox in the dialog) to see all of the points.
You can also use the Reset option in the sectioning dialog to restore the active state on all data
points in all data sets, in order to see all of the data.
If you revert to a sectioned level, you may need to use the Include Inactive Data in Scaling option
in the toolbar of the graph (or the Show Inactive checkbox in the dialog) to see all of the points.
You can also use the Reset option in the sectioning dialog to restore the active state on all data
points in all data sets, in order to see all of the data.
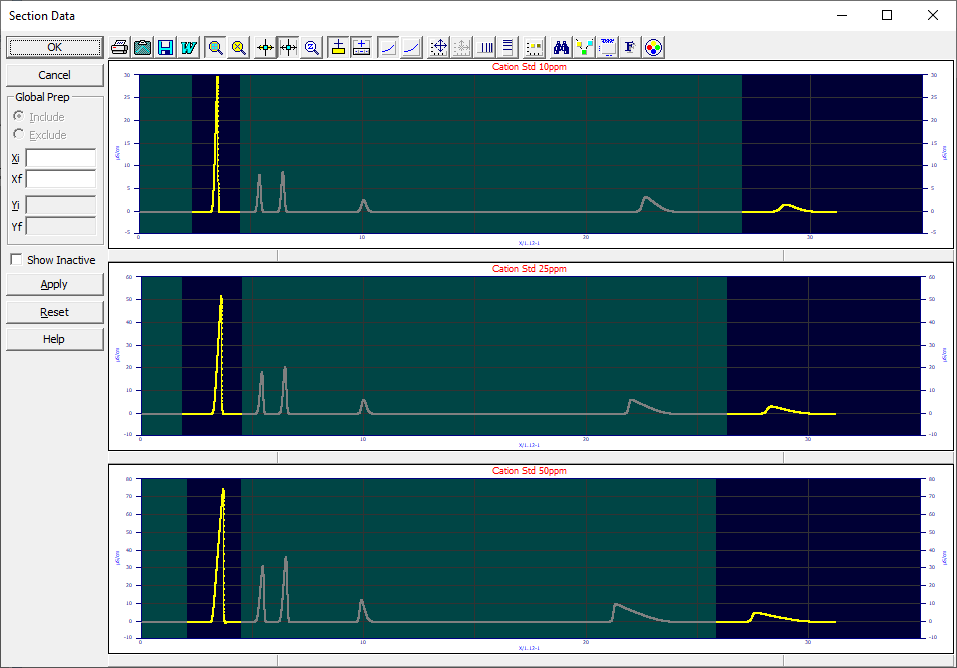
Numeric Sectioning
When you know exactly which ranges to include or exclude, numeric sectioning may be simplest. The sectioning can be set to either Include or Exclude the points in the specified region. A sectioning region consists of 2D box which is defined by an initial Xi, a final Xf, an initial Yi, and a final Yf. If no entries are made for a given variable, the program assumes the full range of the variable when including points, and no range on the variable when excluding points.
To apply the numeric sectioning to the data, you must click the Apply button. The Apply option resets all points prior to the sectioning. If multiple data sets are present, the Apply option will process all sets. If you will be using a global sectioning for most but not all of the data sets, you should first apply the global sectioning before custom sectioning the individuals sets.
![]() If the peaks for one of more of the globally sectioned data sets are not fully visible for local sectioning,
you can use the Include Inactive Data in Scaling option in the toolbar of the graph. You can use
the right click menu option on that particular graph and choose the Reset this Data Set - Clear Sectioning
option and then use the mouse to get the local sectioning desired.
If the peaks for one of more of the globally sectioned data sets are not fully visible for local sectioning,
you can use the Include Inactive Data in Scaling option in the toolbar of the graph. You can use
the right click menu option on that particular graph and choose the Reset this Data Set - Clear Sectioning
option and then use the mouse to get the local sectioning desired.
![]() If the Manual Sectioning mode is selected in the graph's toolbar, the Yi and Yf values
can also be set. Use caution when setting the Y value bounds, especially when multiple data sets are present.
While peak-fitting and most transformations do not require uniformly-spaced x-data, certain procedures,
such as the Fourier deconvolution do require such.
If the Manual Sectioning mode is selected in the graph's toolbar, the Yi and Yf values
can also be set. Use caution when setting the Y value bounds, especially when multiple data sets are present.
While peak-fitting and most transformations do not require uniformly-spaced x-data, certain procedures,
such as the Fourier deconvolution do require such.
Note that local sectioning of a specific data set within multiple sets is always done graphically.
Graphical Sectioning a Range of Peaks
![]() For visual sectioning of an x-range of peaks, be sure the PeakLab
graph is in X-Range Sectioning mode in the graph's toolbar.
For visual sectioning of an x-range of peaks, be sure the PeakLab
graph is in X-Range Sectioning mode in the graph's toolbar.
This mode allows you to use the mouse to box the peaks of interest. This is the default sectioning mode. Click and hold the left button down while boxing the peaks of interest. Release the mouse when the desired peaks have been enclosed in the rectangle. Only the X-values are used for the sectioning and these are placed in the Xi and Xf fields, and only that specific data set is initially sectioned by the graphical procedure. If you are processing multiple data sets, and this one visual sectioning is applicable to all of the data sets, click the Apply button to have this x-range automatically applied to each of the data sets.
To reset just the sectioning in a single graph, right click that graph and select the Reset this Data Set - Clear Sectioning option.
![]() You can use the zoom mode to temporarily zoom-in the range for more accurate sectioning. Remember to reselect
the sectioning mode you are using as soon as the graphs have the detail you need. At any point you can
right click any graph and select the Restore Scaling - Undo Zoom option to restore the automatic
scaling.
You can use the zoom mode to temporarily zoom-in the range for more accurate sectioning. Remember to reselect
the sectioning mode you are using as soon as the graphs have the detail you need. At any point you can
right click any graph and select the Restore Scaling - Undo Zoom option to restore the automatic
scaling.
Manual Sectioning
![]() To manually section the data using the mouse, select the Manual Sectioning mode in the graph's
toolbar. To exclude points, simply place the mouse cursor at the initial point to be excluded, click and
hold the left mouse button down, and slide the mouse to the right. As you do so, the points will be grayed
(indicating that they have been deactivated or excluded). Once the left mouse button is released, the
graph's background will reflect the sectioning.
To manually section the data using the mouse, select the Manual Sectioning mode in the graph's
toolbar. To exclude points, simply place the mouse cursor at the initial point to be excluded, click and
hold the left mouse button down, and slide the mouse to the right. As you do so, the points will be grayed
(indicating that they have been deactivated or excluded). Once the left mouse button is released, the
graph's background will reflect the sectioning.
To reinstate a band of points, simply start at the rightmost point desired, click and hold the left mouse button down, and slide the mouse to the left. As you do so, the points will be restored to an active state.
Caution
This option allows you to section only the peaks you wish to fit. There is no requirement the peaks or data be contiguous. You can exclude one or more peaks, or multiple bands of peaks, in the middle of the data that is to be fitted. When this is done, the x-values will no longer be equally spaced. There may be massive blocks of missing data. You must not use any Fourier preprocessing step after such a sectioning. Fourier deconvolution and Fourier filtration will definitely not work. Fitting any <irf> model similarly will fail, since these fits occur in the Fourier domain and Fourier methods are used in attaining the initial IRF estimates. There may also be issues with peak placements and initial estimates since the Savitzky-Golay smoothing algorithm, used by default, assumes uniformly spaced data.
If you are fitting closed form (no <irf>) models, you will probably be fine. If the local maxima peaks placement algorithm is having trouble with unevenly spaced x-data data, you will need to use the Hidden Peaks - Residuals fitting option with the Loess smoothing algorithm (it does not require equally spaced x values).
Possibly a better alternative, and your only option if fitting an IRF convolution integral, is to assign the unwanted peaks or data features as baseline and remove them using the non-parametric baseline in the Subtract Baseline option. This preserves the equally spaced x-values. You will probably want to use the Zero Baseline postprocessing to ensure zero values for all regions to be excluded from the fit.
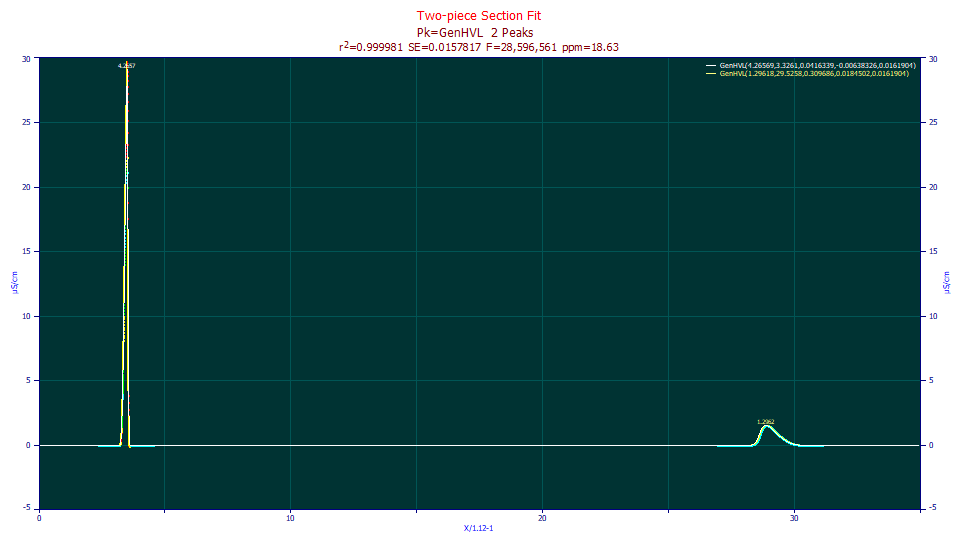
This is a fit of a closed form GenHVL to data that was first preprocessed in transform, baseline, and IRF deconvolution steps, prior to the first and last peak being isolated by sectioning. There is a massive empty zone of missing data, but the non-linear fit is unaffected.
Graphical Toggling of Points
![]()
![]() To toggle a single point between active and inactive, the PeakLab
Graph must be in one of the sectioning modes. In either mode, simply place the mouse cursor on the
point desired. The mouse cursor will change to a crosshair with a point in its center. If you have the
hints active, the hint color will change and indicate the point under the cursor. If the graph's status
bar is active, you will see the point under the cursor also indicated there. Simply click the left mouse
button without moving the mouse to toggle the point on or off.
To toggle a single point between active and inactive, the PeakLab
Graph must be in one of the sectioning modes. In either mode, simply place the mouse cursor on the
point desired. The mouse cursor will change to a crosshair with a point in its center. If you have the
hints active, the hint color will change and indicate the point under the cursor. If the graph's status
bar is active, you will see the point under the cursor also indicated there. Simply click the left mouse
button without moving the mouse to toggle the point on or off.
The same caution applicable to manual sectioning applies to this form of introducing non-uniform x-data.
Zoom-Mode
![]() For better clarity or definition, you may wish to zoom-in a given region prior to sectioning. The zoom-mode
is provided for this purpose. The graph can be zoomed in this mode by simply clicking and holding down
the left mouse button while enclosing the zoom-in region desired. Remember to reselect the sectioning
mode you are using as soon as the graphs have the detail you need. At any point you can right click any
graph and select the Restore Scaling - Undo Zoom option to restore the automatic scaling.
For better clarity or definition, you may wish to zoom-in a given region prior to sectioning. The zoom-mode
is provided for this purpose. The graph can be zoomed in this mode by simply clicking and holding down
the left mouse button while enclosing the zoom-in region desired. Remember to reselect the sectioning
mode you are using as soon as the graphs have the detail you need. At any point you can right click any
graph and select the Restore Scaling - Undo Zoom option to restore the automatic scaling.
To restore normal scaling, simply click the right mouse button anywhere within the graph region.
Reset
The Reset button restores all data points, in all data sets, to an active state.
Accepting the Sectioning
Exit the dialog with OK to accept the sectioning shown in the graph, or Cancel to exit without adopting any modifications.
Multiple Data Sets
If you have multiple data sets present, all will be shown in this procedure, irrespective of whether or not a data set is selected in the main window of the program. The data set selection in the main screen applies only to the View and Compare Data options and the Local Maxima Peaks, Hidden Peaks - Residuals, and the Hidden Peaks - Second Derivative fitting options.
With all data sets shown, exit the dialog with OK to accept the sectioning shown in the graphs, or Cancel to exit to abandon the sectioning.
To section a specific data set, double click that graph (or right click and select the Plot This Data Set option from the popup menu). After graphically sectioning the data, you can click OK, double click the graph, or right click the graph and choose Plot All Data Sets from the popup menu to restore the display of all data sets. Clicking OK when you are within a single plot returns you to the dialog with all data sets rendered.
Sections are saved by their point by point data states.
Show Inactive
The Show Inactive checkbox will scale for both the inactive and inactive points, allowing all of the data to be seen, regardless of it sectioned state. Uncheck this box to scale the graphs for the sectioned points.
![]() You can also use the Include Inactive Data in Scaling option in the toolbar of the graph.
You can also use the Include Inactive Data in Scaling option in the toolbar of the graph.
Right Click Menu Options
When you right click a graph a popup menu will offer the following options:
Restore Scaling - Undo Zoom
If you have zoomed in the graphs, this option can be used to undo the zoom-in and restore the automatic scaling.
![]() If the Zoom-In Applies to All Graphs is selected in the toolbar, the zoom will apply to all graphs
controlled by that toolbar. Both the x-range and y-range of the zoomed graph will be transferred to all
of the other graphs.
If the Zoom-In Applies to All Graphs is selected in the toolbar, the zoom will apply to all graphs
controlled by that toolbar. Both the x-range and y-range of the zoomed graph will be transferred to all
of the other graphs.
![]() If the Zoom-In Applies to All Graphs, X-scaling only is selected in the toolbar, the zoom will
apply to all graphs controlled by that toolbar, but only the x-range will be transferred to the other
graphs.
If the Zoom-In Applies to All Graphs, X-scaling only is selected in the toolbar, the zoom will
apply to all graphs controlled by that toolbar, but only the x-range will be transferred to the other
graphs.
If neither option is selected, the zoom will apply only to the one graph where the zoom was made.
Plot this Data Set
Use this right-click menu option to view or independently graphically section just one of the data sets.
Plot All Data Sets
You can use this right-click option to close a local sectioning or viewing step. You can also close the local sectioning by clicking OK-the dialog is restored to where all data sets are shown. You can also double click the graph to restore all data plots. In all cases, the locally sectioned data will be preserved.
PeakLab Graph
All of the graph options are available in the PeakLab graph which is used throughout the program.
Sectioning only a Single Data Set
In order to section an individual data set when multiple data sets are present, it may be more convenient to invoke the sectioning by right clicking the data set of interest in the main program window and selecting Independently Section this Data Set from the popup menu.


 |